Introduction:
Hey Folks! Am Vishwa and am currently learning DevOps with the help of OpenSource and Communities. I learned Computer Networks recently and I made a Blog on that. Part-1 was published already, you can check it. Now this Blog is
Part-2 of Computer Networks In this you will learn about Protocols like TCP/IP, UDP/IP, Telnet and some Web Protocols then about Sockets, Ports, Error/Status codes, Cookies and How Mail works then about DNS.
Protocols:
This is nothing but a set of rules for data transferring between networks.
TCP/IP , UDP/IP (User Datagram Protocol/Internet Protocol), Telnet.
Web Protocols:
1. TCP/IP:
It stands for Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol. It is used as a communication protocol to interconnect between network devices on the Internet as well as used in Private computer networks too.
In this, we’ve certain protocols like HTTP, HTTPS, DHCP, FTP, SMTP, POP3 and IMAC, SSH, and VNC.
HTTP:
HTTP stands for Hyper Text Transfer Protocol. It is used at the Application layer and it is a Stateless protocol, stateless means Server won’t store any information about the Client by default. Every application layer may require some Transport layer protocol, and it makes sure that all are received successfully. HTTP uses a Transport layer inside it. HTTP methods are nothing but telling what to do, and they are Get, Post, Put, and Delete.
HTTPS:
HTTPS stands for Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure. It is nothing but HTTP with encryption and verification, it uses TLS-Transport Layer Security (SSL-Secure Socket Layer) to encrypt HTTP requests and responses. It is far more secure than HTTP to prevent data from attackers. It is a primary protocol used to send data between a web browser and a website.
DHCP:
It stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. It is used in giving IP addresses to the connected devices. The Modem/Router connected to the ISP will have a Global IP and that Modem or Router will assign IPs for the connected devices with the help of DHCP.
FTP:
It stands for File Transfer Protocol. It is a Network protocol used for transmitting data between Computers over TCP/IP connections. In TCP/IP, FTP is considered an Application Layer. Ability to resume a file transfer, if the connection is lost and it put items into a queue to be uploaded or downloaded.
SMTP:
SMTP stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. It is used to send and receive mail, mostly it combines and works with IMAP or POP3 for receiving because its primary task is to send mail.
IMAP or POP3:
IMAP stands for Internet Messaging Access Protocol and POP3 stands for Post Office Protocol. These two are used to retrieve messages whereas SMTP only focuses on sending.
SSH:
SSH stands for Secure Shell. SSH is nothing but a network protocol for communicating between two computers and sharing data. It gives users, particularly system admins to have a secure way for accessing a computer over an unsecured network.
VNC:
It stands for Virtual Network Computing. It is used as a type of remote-control software that makes it possible to control another computer over a network connection.
2. UDP/IP:
It stands for User Datagram Protocol/Internet Protocol.
It is a Stateless connection, which means that the data we transfer might be lost and there is no worry about it.
Example: Video Conferences.
3. Telnet:
It stands for Teletype Network and it was developed in 1969. A CLI to communicate between servers or devices.
It enables the user to work remotely over the Internet (Still many peoples are using it to access computers remotely over TCP/IP).
It is a network as well as application protocol that provides two-way (Collaborative) and text-based communication between two machines.
Sockets:
It is nothing but an interface between the process and the internet. It is an endpoint of a two-way communication link between the programs running on the network.
Ports:
It is used to identify which process needs the output, IP address identifies which device whereas the Port identifies which application.
Now there might be a chance of multiple tabs opened in Chrome (Application), so in this case it uses Ephemeral Ports, it exists on Client Side. When a client requested internally the server will use ephemeral ports.
Error/Status Code:
When we request to the server, we want to know whether the request is successful or not, for this it is used.
Example:
200 means Request was successful. 404 means could not find it. 400 means a Bad request. 500 means an internal server error. Range of Status Codes:
Note: If it lies in the 100 range then it is in Informational Category, the 200 range means Server Codes, the 300 range means Redirecting Codes, the 400 range means Client error (Something that we did), and the 500 range means a Server error.
Cookies:
These are called Unique String, files that are stored in my Browser. The server will know who is contacting and cookies have expiration dates also.
ThirdParty Cookies: It is nothing but cookies set for the URL that we have not visited.
How Email Works:
Email stands for Electronic Mail. For sending email, it uses SMTP and for receiving email, it uses POP3 or something like IMAP.
Email uses TCP for transferring.
How does it work?
For mail: for example yahoo.com to google.com, it uses the following way.
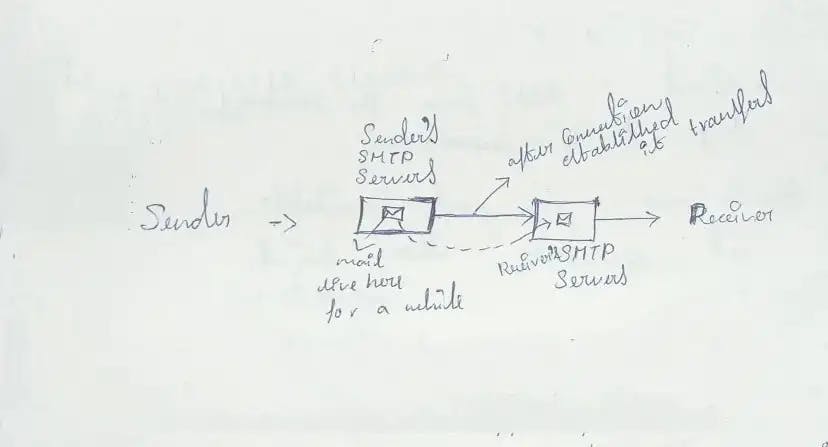
If it is Gmail to Gmail means this connection won't happen. Sometimes Error handling will happen or it is required for the message not to be delivered. Example: If the receiver’s server is offline means, the sender server will keep on trying before it gives up.
Use nslookup command (nameserver lookup) to find the Name and the IP of the SMTP servers for various domains like Gmail, and Yahoo.
Command: nslookup -type=mx gmail.com
For downloading E-Mails:
1. POP:
It uses POP(Post Office Protocol) for downloading.
The client connects to port 110 which is allocated for POP and it asks the server to give all the mails.
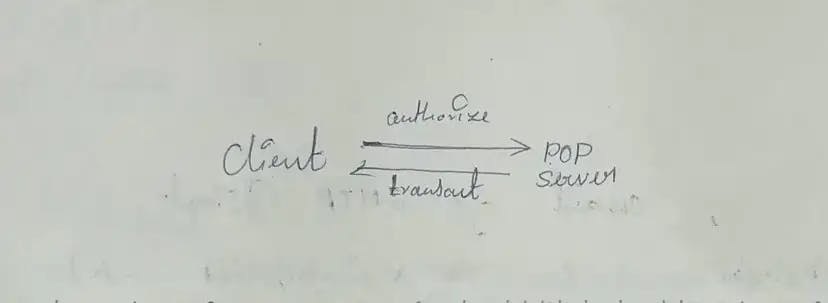
Others like sent and draft folders are not synced with the POP server. We can download or deletes from the server or we can keep it in the server. If it is deleted in the server, it is only available on the Client not on any other devices.
2. IMAP:
IMAP(Internet Message Access Protocol) is used to get Mails.
It is a little bit complex but allows us to view the emails on multiple devices.
This is all about Email, How it works and its various protocols.
DNS:
It is nothing but a Domain name System. A simple example is Every civilian has ID proof that every domain has its IP address.
Where it is stored and How does it find? The solution is DNS.
When we type google.com, it uses DNS to find the Google server. After typing google.com, HTTP takes this URL and finds the server using DNS and connects with it. IP will be stored in some Databases, once we ask for the request, it gives the required solution for the URL.
The domains are divided into various types of classes.

The top ones are root DNS servers. It is the first point of contact(ISP).
Example:
TLD (Top Level Domain): .io / .com / .org
SLD (Sub Level Domain): student.io / google.com / commclassroom.org
By visiting root-servers.org, we can check who is maintaining the DNS servers.
.com is for Commercial Organizations,
.edu is for Educational Institutions,
.org is for Non-Profitable Organizations,
.uk or .us is for Country Specific.
These TLD are maintained by ICANN(Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers). We cannot but any domain name, we can rent it.
If we search for Something,
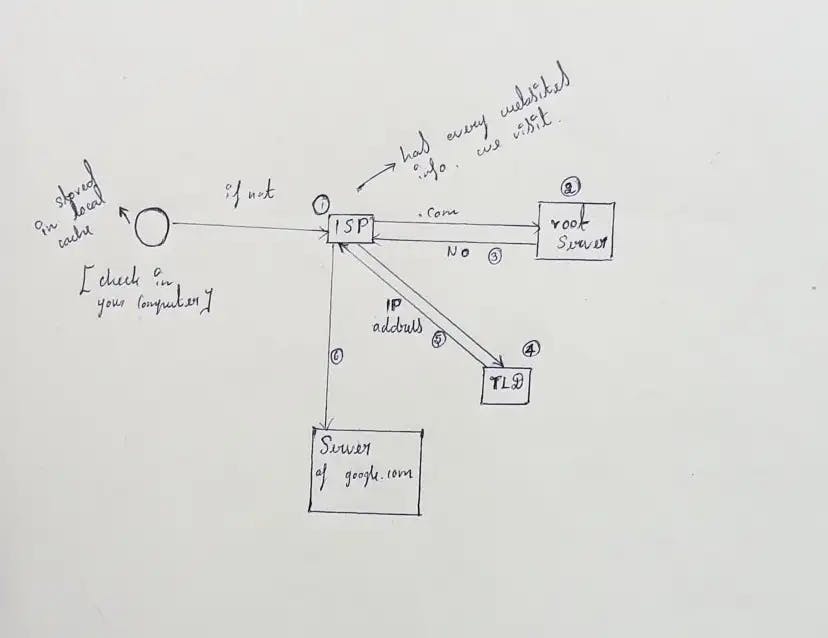
By using dig command, we can see the message’s received from the DNS server. Example: Type dig google.com in terminal.
Note: Sometimes this dig command wont work, for that we’ve to set Path. You can check it in google.
This is all about Part-2 of Computer Networks. In Part-3, we will see about Transport layer and its protocols like UDP, TCP then Three-way handshaking and about Network layer then IPv4 and IPv6.
Thanks for Reading Folks!

